Authentication of small diamonds
Since 2004, the Swiss Gemmological Institute – SSEF checks the authentication and the quality of colourless small diamonds (melee) batches for many luxury watchmaking and jewellery manufacturers in Switzerland abroad.
ASDI – Automated Spectral Diamond Inspection is a highly specialised instrument developed by SSEF that enables the screening of melees at a high speed and reasonable price.
Toolbox
Quality control of small diamonds
The Swiss Gemmological Institute SSEF has set up a strict protocol for the quality control of colourless small diamonds (melees and baguettes), fitting with specific requirements of the watch- and jewellery industry. The detailed information available on SSEF reports help our clients to evaluate the quality of their lots of small diamonds and maintain their quality management. Our routine ensures the best reproducibility of results and provides our clients results they can trust.
We routinely control colour, clarity and cut quality of small diamonds. Each diamond that is subject to quality control is also authenticated using the ASDI instrument, with the aim of sorting out any and every synthetic diamond or diamond imitation.

Colour
- Each small diamond is placed table down in a white folded paper under a normalised light.
- Each small diamond is compared to our CIBJO diamond Masterstones.
- When checking the colour of a small diamond it is important to compare it to a large diamond masterstone. This reduces colour grading margin errors, as opposed to the comparison with a small diamond masterstone.
Clarity
- A sortoscope microscope is used for the clarity control of small diamonds and enables the visual control of a large quantity of small diamonds.
- The size of an inclusion may be measured with a special eyepiece.
- Stones may be compared with SSEF clarity master stones.
- The final purity grade is defined by means of the 10x loupe.
Cut (symmetry, polish, proportions)
- SSEF has created a Symmetry Masterset for small diamonds. This Symmetry Masterset groups more than 30 selected diamonds from an ‘Excellent’ to a ‘Poor’ symmetry grade.
- For evaluating the symmetry grade of a diamond we check : roundness ; eccentric or tilted or wavy tables, truncated or short facets, facets of unequal size, edge displacement ; girdle with unequal thicknesses, etc.
- SSEF has created a Polish Masterset for small diamonds. It groups more than 8 selected diamonds from «Excellent» to «Poor» polish grade.
Toolbox
Pricing for quality control of melees: sampling basis (English and French) or 100% quality control (English and French)
Pricing for quality control of baguettes: 100% quality control (English and French)
Sample reports for a batch of small diamonds may be found here in French: full lot tested (PDF) or random sampling (PDF)
*Please also note the terms & conditions for submission for quality control of small diamonds in French (PDF)
Explore our research library
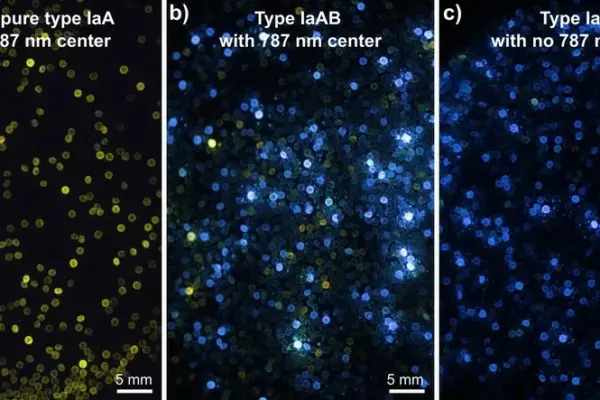
Nickel-bearing type IA natural colourless diamond
In gemmology, nickel is generally associated with synthetic HPHT diamonds through the presence of the well-known nickel-related (Ni-related) centre at 883/885 nm, which is rarely present in natural diamonds.
A descriptive study on as-grown and HPHT-treated CVD synthetic diamonds
The Swiss Gemmological Institute is testing more than one million colourless melee diamonds for the Swiss watch and jewellery industry on an annual basis to guarantee that no synthetic diamonds are mixed within natural melee diamond batches.
Jean-Pierre Chalain: over 3 decades of diamonds at SSEF
On March 31st 2024, Jean-Pierre Chalain – director of SSEF’s diamond department- retired from SSEF and handed over the diamond department to Dr. Michael Mintrone and his team.
A study of nickel-bearing type Ia diamonds
A study of nickel-bearing type Ia diamonds. IGC 2023 Proceedings, 37-39.
Pearls & diamonds: a royal selection
The SSEF is known worldwide as a leading authority in gem testing, and as such we have the great pleasure to scientifically analyse some of the most prestigious and important jewellery before it is offered up for auction or in private sales. Apart from testing the gem materials in such jewellery, we
Synthetic moissanite with reflectivity of diamond
Synthetic moissanite with reflectivity of diamond. The Journal of Gemmology, 38(4), 323-325.
ISO standards in the diamond trade: history and benefits (2022)
Presentation at the 2022 Rendez-Vous Gemmologiques de Paris Conference by Jean-Pierre Chalain (original version of this presentation was in French, this version has been translated into English)
Diamond fraud uncovered
As in the past, the SSEF is regularly asked by the Swiss police authorities to act as a gemmological adviser in criminal cases. Usually, these are fraud cases, involving undeclared or mislabeled gemstones or their imitations. In a recent case with about 20 stones submitted by the police, we not only
A new led daylight source for diamond colour grading
In 2020, a novel light source for the colour grading of diamonds was developed in a collaboration between SSEF and the Department of Physics, University of Basel (see Figure 1). In contrast to many of the models on the market, the new light source uses state-of-the-art LED (Light Emitting Diode) lig
Two exceptional asteriated diamonds
by Dr. L. Speich & J.-P. Chalain, first published in Facette 27 (June 2021) Recently, SSEF received two so-called asteriated diamonds for authentication. Asteriated diamonds are rare and highly prized amongst collectors for their beautiful and unique appearance. The two stones received
Preliminary study of defocused PL measurements of diamonds
A study of nickel-bearing type Ia diamonds. IGC 2023 Proceedings, 37-39.
Treated greenish yellow diamond with brown radiation stains
Treated greenish yellow diamond with brown radiation stains. The Journal of Gemmology, 680-683.
Authors